What is Sustainable Waste Management?
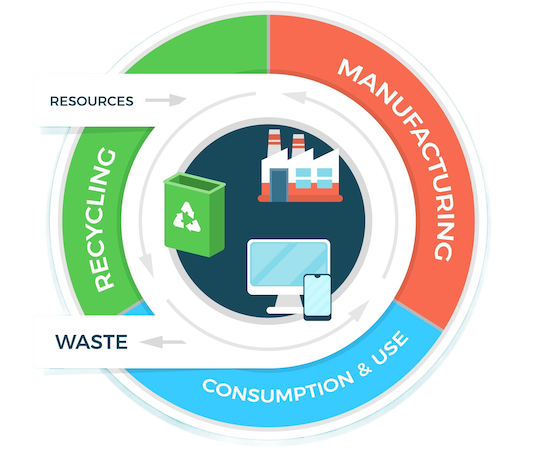
Sustainable waste management takes a broad view. It aims to lessen waste’s impact on the environment. It pushes for less waste, reuse, recycling, and better recovery of waste materials. This forms a key part of the circular economy. The goal? To keep resources in use as long as possible. To get the most value from them. Then, we need to recover and give new life to products and materials when they’re done. This stands in stark contrast to the old-school linear economy. That one follows a take-make-throw-away model.
To tackle these issues, Malaysia needs to change its approach to waste management. It should be more joined-up and long-lasting. This means better recycling setup, raising the public’s awareness, and implementing tougher rules on throwing away and recycling waste.
By turning waste management problems into opportunities, Malaysia can prepare for a more sustainable and resilient future.
The Waste Management Hierarchy
The waste management hierarchy offers a structure to rank solid waste management methods for the best environmental results.
Reduce
Cutting down on waste where it starts works best to handle trash. Here are some ways to make less garbage:
- Design items to use less material.
- Make things better, so there’s less waste.
- Get people to buy what they need and pick items without much packaging.
For example, car factories now use smart methods to cut down on wasted materials. Farms use exact science to grow food with less going to waste. Stores that sell things without packaging help cut down on trash, too.
Reuse
Making products and materials last longer by using them again plays a key role in managing waste. People can fix things, buy and sell used items, and turn waste into new, handy items. In Malaysia, programs like KitaRecycle push people to give away things they can reuse instead of throwing them out. Also, community repair shops give people places to bring broken items for volunteers to fix.
Recycle
Recycling turns trash into new products, reducing the need for raw materials and saving energy. Here are some good ways to recycle:
- Sorting items that can be recycled from those that can’t when throwing things away.
- Teaching people why recycling matters.
- Using high-tech sorting plants to handle recyclable stuff.
In Malaysia, recycling has problems like different methods in different places, insufficient needing more equipment, and few people taking part. Still, recycling has a big impact on waste management. It helps use less landfill space and save resources.
Recovery
Getting energy back from trash using methods like waste-to-energy plants and landfill gas recovery plays a key role in the waste plan. Waste-to-energy plants turn trash we can’t recycle into usable energy by burning it or letting bacteria break it down without oxygen. Landfill gas recovery catches methane gas from dumps to make electricity. These energy recovery techniques shrink landfills and create renewable power, which helps save resources and cut down on fossil fuel use.
Treatment and Waste Disposal
Proper handling and getting rid of dangerous and regular waste play a key role in reducing environmental harm. Hazardous waste needs special methods to treat it, like using chemicals to make it harmless, burning it, or putting it in secure dump sites. Regular waste can be dealt with by turning it into compost, recycling it, or putting it in regular dump sites. When waste isn’t thrown away, it can cause pollution, making the air, water, and ground dirty. This poses health dangers to people and animals. It also adds to the gases that warm up the planet, worsening climate change.
Innovative Technologies in Waste Management
Smart Waste Management Solutions
Smart waste management solutions use the Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) to improve waste collection and processing productivity. For example, smart bins with IoT sensors can keep track of fill levels as they happen and tell waste collection services when they need emptying. This data-based method helps make collection routes better, cutting down on extra trips and gas use. Also, AI can sort waste more efficiently, boosting recycling rates and reducing contamination. Using these technologies impacts cost savings, less environmental harm, and better public health through more effective waste management practices.
Advanced Recycling Techniques
New recycling methods use better tech than old-school mechanical recycling. These include chemical recycling, which turns plastics into their basic building blocks, and heat-based processes like pyrolysis, which changes waste into useful chemicals and fuels. In Malaysia, new high-tech plastic recycling plants are helping to tackle the country’s trash problems. Around the world, nations use these technologies to boost recycling and reduce landfill use. These new methods don’t just make recycled stuff better – they also let us recycle more materials, leading to a greener way of dealing with waste.
Circular Economy Models
The circular economy keeps resources in use as long as possible by focusing on reducing, reusing, and recycling. This model differs from the traditional linear economy, which follows a take-make-dispose approach. A circular economy aims to minimize waste and design products to be reused, repaired, or recycled back into production. Gargeon, a Malaysian company, helps the shift to a circular economy by offering new waste management solutions that incorporate these ideas. Using circular economy models, Malaysia can lower its environmental impact, open up economic chances, and move toward a more sustainable future.
Sustainable Waste Management Practices Across Industries
Healthcare Industry
The healthcare industry has to deal with unique waste management problems because of the different types of waste it creates, such as hazardous medical, pharmaceutical, and infectious waste. To stop contamination and keep the public safe, separating, collecting, and eliminating waste is essential. Some answers to this problem include using secure, leak-proof containers for dangerous waste and putting in place strict rules for handling and throwing away infectious materials. Good practices involve:
- Training staff on how to manage waste.
- Keeping accurate records.
- Following regulatory standards to lower risks and protect public health and the environment.
Hospitality and Tourism
The hospitality and tourism sector produces a lot of waste. This includes leftover food, disposable plastics, and cleaning chemicals. To deal with this waste, businesses can:
- Start recycling programs.
- Cut down on single-use plastics.
- Give guests options to reuse bedding and bathroom items.
Turning food scraps into compost can help local farms. In Malaysia, some places are trying to be more eco-friendly. For example, in Lower Kinabatangan and Sabah, locals participate in nature-based tourism. This approach helps protect the environment and encourages responsible travel.
Retail and Consumer Goods
The retail and consumer goods industry can reduce packaging waste by using sustainable packaging options, like materials you can recycle or that breakdown. Companies can also push for less packaging and sell products you can refill to waste reduction. In Malaysia, quite a few companies have put eco-friendly practices into action. For example, The Hive Eco Store, it promotes shopping without waste by selling unpackaged, organic waste, and local food items. Then there’s The Green Factory, which sells eco-friendly household products and bags you can use repeatedly. These efforts don’t just cut down on waste – they also strike a chord with customers who care about the environment, which boosts brand image and keeps customers coming back.
Policy and Regulatory Framework in Malaysia
Government Initiatives and Regulations
Malaysia has put in place a thorough set of rules to handle waste effectively and effectively. The main part of these rules is the Environmental Quality Act of 1974. This act controls how to stop, cut down, and manage pollution. It also aims to improve the environment. The act has specific rules for dealing with certain types of waste. One example is the Environmental Quality (Scheduled Wastes) Regulations 2005. These rules define how to handle, treat, and eliminate dangerous waste.
On top of these rules, Malaysia’s government has started several programs to back sustainable waste management. The Twelfth Malaysia Plan (12MP) for 2021-2025 wants to reach a National Recycling Rate (NRR) of 40% by 2025. This plan stresses the need for a circular economy, pushing businesses to use sustainable design, production, logistics, consumption, and waste management methods. Another key program is the Circular Economy Blueprint for Solid Waste (2025-2035), which has steps like Extended Producer Responsibility and Pay-As-You-Throw plans to cut down waste and boost recycling.
Compliance and Certification
Following local and international rules plays a big role in ensuring waste management works well and lasts. Sticking to these rules helps companies reduce harm to the environment, follow the law, and look better to others. ISO 14001 stands out as a key worldwide standard. It provides a plan for setting up a good Environmental Management System (EMS). This standard aids companies in handling their duties to the environment in an organized and long-lasting way.
In Malaysia, a few certifications play a role in sustainable waste management. For instance, the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC®) certification ensures forest products come from well-managed forests. These forests offer benefits to the environment, society, and economy. The B Corporation certification is another key player. It looks at how well a company performs in social and environmental areas. These certifications show a company’s dedication to sustainability. They also help businesses earn customer trust and meet the needs of international markets.
Gargeon’s Approach to Sustainable Waste Management
Our Services and Solutions
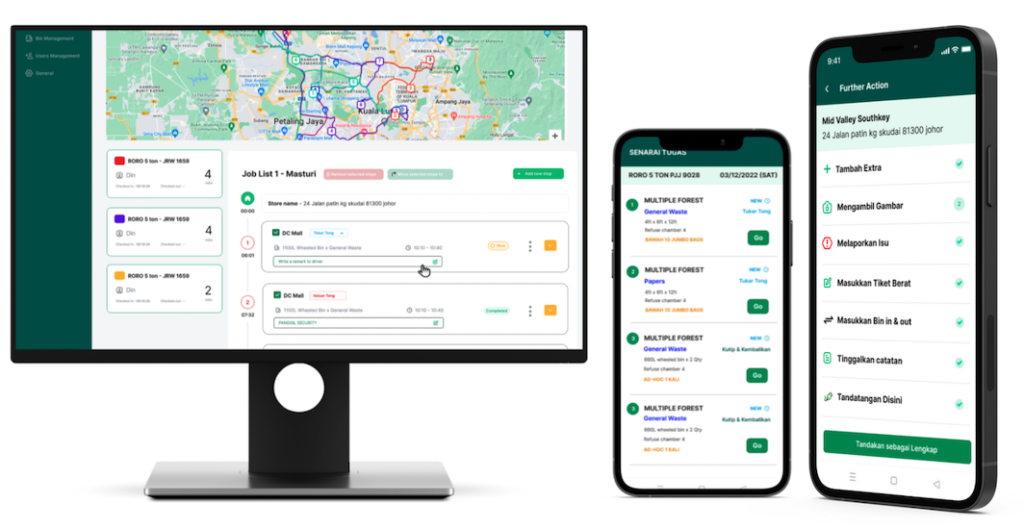
Gargeon provides wide-ranging waste management services and tech to improve waste collection, processing, and recycling. The heart of what Gargeon offers is a cloud platform that turns waste management tasks digital, giving companies up-to-the-minute insights into their waste flows. This platform has features like smart bins with IoT sensors to monitor how full they are, auto-scheduling for trash pickup, and cutting-edge sorting tech powered by AI to boost recycling productivity. Using these tools, Gargeon helps companies cut down on waste, keep more money in their pockets, and run their operations more.
Gargeon crafts solutions that match global best practices and local needs. It follows international standards like ISO 14001 for environmental management systems, which ensures its services meet tough sustainability benchmarks. Also, Gargeon teams up with local waste collectors and recycling plants to ensure its solutions work well and fit the Malaysian scene. This method boosts the long-term viability of waste management practices and lifts local economies and communities.
Commitment to Sustainability
Gargeon believes in making waste management more eco-friendly. The company wants to create a world that produces less trash, saves resources, and reduces harm to the environment. To make this happen, Gargeon tries to keep as much waste as possible out of landfills, pushes for more recycling and reusing, and backs the move to an economy that wastes less. Their goal is to help businesses find value in their trash by cutting down on actual waste and saving time, money, and energy.
In the future, Gargeon has plans for several new projects and fresh ideas to push its sustainability goals even further. These include rolling out its smart waste management fixes to more industries, coming up with new ways to turn waste into energy, and beefing up its data-crunching skills to give even more in-depth insights into waste management practices. By always coming up with new ideas and adjusting to changing environmental challenges, Gargeon wants to be at the forefront of sustainable waste management and help create a greener, more sustainable future.
Challenges and Opportunities in Sustainable Waste Management
Alt text: household waste
Current Challenges
Putting sustainable waste management strategies into action in Malaysia runs into some big roadblocks. One of the main problems is that waste is piling up fast as cities grow and more people move in. This flood of trash puts a lot of stress on the current waste handling systems, which often need to catch up with all the garbage. Also, Malaysia relies too much on dumping trash in landfills, which causes environmental trouble, such as dirty soil and water, and pumps out gases that heat the planet.
Socioeconomic and cultural factors have a big impact on how we handle waste. People don’t often participate in recycling programs or know much about them. This happens because they haven’t learned enough about why sorting waste and recycling matter. Money issues also make things harder. Using new, better ways to manage waste costs a lot, and local governments often can’t afford it. This makes it tough to start using practices that are good for the environment. The way people think about waste in their culture is another problem. Many prefer what’s easy over good for the planet, slowing progress.
Opportunities for Growth and Innovation
Despite these challenges, waste management has many chances to grow and introduce new ideas. One area that could be improved is using advanced recycling tech. New methods like chemical recycling and pyrolysis can turn waste into useful stuff, cutting down on landfill use and helping create a circular economy. Also, ways to turn waste into energy offer a lasting solution to handling non-recyclable waste while making renewable power.
Another promising field is bringing in data-driven waste management answers. Techs like IoT and AI can make waste collection and processing work better, making the system more productive and cheaper to run. For instance, smart bins with sensors can keep an eye on how full they are and plan the best routes for pickup, cutting down on running costs and harm to the environment.
Gargeon is in a good spot to take advantage of these changes. Its cloud-based sustainable waste management system and cutting-edge tech give companies up-to-the-minute insights on their waste flows. This helps them improve how they handle waste and cut down on expenses. Gargeon’s dedication to being eco-friendly and forward-thinking keeps it leading the pack in the waste management field. It’s pushing for positive shifts and helping build a more sustainable tomorrow.
Leading the Way in Waste Management Innovation
Alt text: Smart Waste Management
To wrap up, sustainably managing waste is crucial in safeguarding our environment, boosting public health, and driving economic growth. When we stick to the waste management hierarchy—cut down, use again, recycle, recover, and throw away—we can reduce waste and its effects. New tech ideas, like smart waste management answers and cutting-edge recycling methods, are causing a revolution in the industrial waste management, boosting its productivity and sustainability. The circular economy model also stresses how important it is to keep using resources for as long as possible.
Malaysia grapples with distinct waste management issues, such as high trash production, heavy use of landfills, and social, economic, and cultural hurdles. Yet these problems also open doors to progress and new ideas. By using cutting-edge tech and data-based solutions, Malaysia can boost its trash handling methods and head towards a greener tomorrow.
Gargeon leads this change, providing wide-ranging waste management services and technologies that match global standards and local requirements. Their focus on going green and always coming up with fresh ideas puts them at the top of their field.
We urge companies and neighborhoods to collaborate with Gargeon to develop long-lasting trash fixes. If we join forces, we can tackle the big waste generated control problems and build a cleaner, healthier world that lasts for our kids and grandkids.